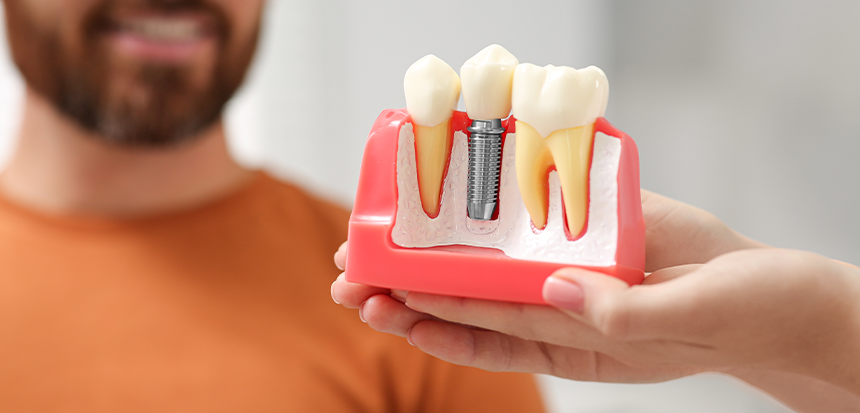
A dental implant is a surgical procedure where artificial tooth roots are placed into the jawbone to replace missing teeth. These implants are made from durable materials designed to function like natural teeth. Implants provide a secure foundation for dental prosthetics and restore natural smile and chewing function.
Dental implants can be performed on individuals who have good oral and jawbone structure, and have a jawbone suitable for implant placement. However, in some cases, inadequate bone density or quality may pose limitations. A dental professional will assess each individual's condition to determine if they are suitable candidates for the procedure.
The dental implant procedure typically involves the following steps:
Examination and Evaluation: The dental professional assesses the individual's oral and jawbone condition and creates a suitable implant placement plan.
Surgical Procedure: Under local anesthesia, a dental implant, resembling a screw, is inserted into the jawbone.
Healing Process: The implant begins to integrate with the jawbone through a process called "osseointegration," which can take several months.
Temporary Prosthesis: A temporary dental prosthesis may be placed during the healing period.
Permanent Prosthesis: After the implant has healed, a custom-made permanent dental prosthesis is attached.
While dental implant procedures are generally safe and successful, like any surgical procedure, they carry some risks. Common risks include infection, implant-bone incompatibility, and inadequate bone density. However, these risks can be minimized with proper care and when the procedure is performed by a skilled dental professional.